Dow Jones Industrial Average keeps the bearish note ahead of US inflation
- Wall Street turns lower with investors turning cautious ahead of US CPI release.
- US inflation is expected to show mixed readings with levels well above the Fed’s 2% core target rate.
- The Dow Jones Index has found support at 38,540, although broader bias remains negative.
The Dow Jones Industrial Average (DJIA) has dropped into negative territory during Tuesday’s US morning session. The moderate risk appetite seen during the European trading session has waned in the US, with investors taking a cautious stance ahead of Tuesday’s US CPI release.
US Consumer Inflation is expected to have accelerated to 3.4% in March from the 3.2% annual rate in February. The core CPI, which scraps the impact of seasonal food and energy prices, is estimated to ease to 3.7% from a 3.8% annual reading for February. In any case, showing levels well above the Federal Reserve’s (Fed) 2% core inflation rate for price stability.
The cautious market mood has sent all the main Wall Street indices lower on Tuesday. The Dow Jones drops 0.43% to 38,726, followed by the S&P 500, which is 0.36% down to 5,181, and the NASDAQ Index, 0.28% lower to 16,208.
Dow Jones news
Among sectors, the Financials are getting the biggest blow with a 0.9% loss, followed by the Industrials, 0.6% lower, and Energy, dropping 0.5%. Real Estate is 0.6%, while Utilities and Consumer Staples and Consumer Discretionary are moving about 0.1% higher each.
Travelers Companies (TRV) is the worst-performing stock in the Dow Jones, losing 2.3% to $225.28, followed by American Express (AXP) which is down 1.8% to $219.83. The biggest winners are Cisco Systems (CSCO), up 2.79%, to $49.59, and 3M (MMM), advancing 1.23% to $93.06.
Dow Jones technical outlook
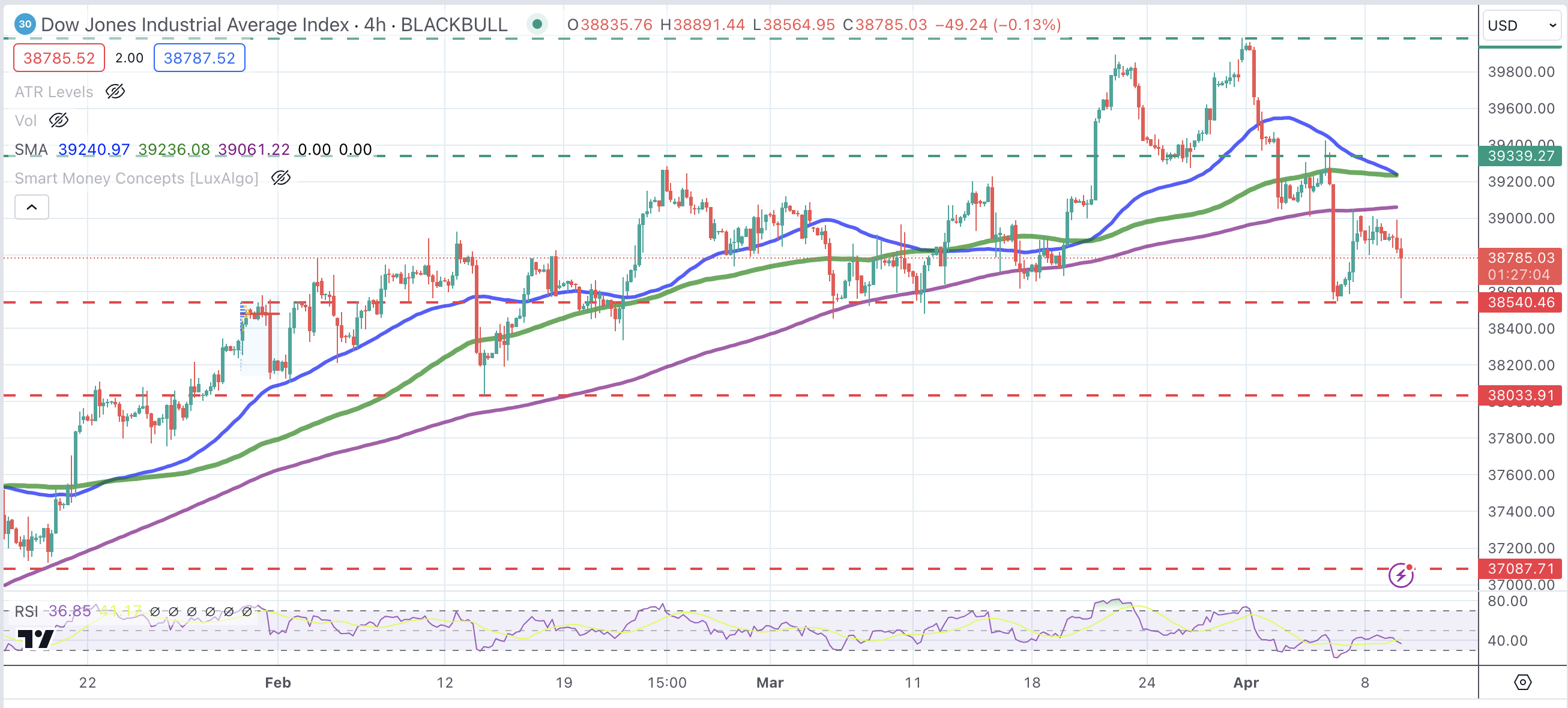
The technical picture shows the Dow Jones index picking up after having tested the support area at 38,540. The broader trend, however, remains bearish with the pair correcting lower from March highs near 40,000.
A further decline below 38,540 would expose February’s low at 38,035. On the upside, the pair should breach the 39,340 resistance area to break the negative price structure and open the path toward the all-time high at 39,985.
Dow Jones Index 4-Hour Chart
Dow Jones FAQs
The Dow Jones Industrial Average, one of the oldest stock market indices in the world, is compiled of the 30 most traded stocks in the US. The index is price-weighted rather than weighted by capitalization. It is calculated by summing the prices of the constituent stocks and dividing them by a factor, currently 0.152. The index was founded by Charles Dow, who also founded the Wall Street Journal. In later years it has been criticized for not being broadly representative enough because it only tracks 30 conglomerates, unlike broader indices such as the S&P 500.
Many different factors drive the Dow Jones Industrial Average (DJIA). The aggregate performance of the component companies revealed in quarterly company earnings reports is the main one. US and global macroeconomic data also contributes as it impacts on investor sentiment. The level of interest rates, set by the Federal Reserve (Fed), also influences the DJIA as it affects the cost of credit, on which many corporations are heavily reliant. Therefore, inflation can be a major driver as well as other metrics which impact the Fed decisions.
Dow Theory is a method for identifying the primary trend of the stock market developed by Charles Dow. A key step is to compare the direction of the Dow Jones Industrial Average (DJIA) and the Dow Jones Transportation Average (DJTA) and only follow trends where both are moving in the same direction. Volume is a confirmatory criteria. The theory uses elements of peak and trough analysis. Dow’s theory posits three trend phases: accumulation, when smart money starts buying or selling; public participation, when the wider public joins in; and distribution, when the smart money exits.
There are a number of ways to trade the DJIA. One is to use ETFs which allow investors to trade the DJIA as a single security, rather than having to buy shares in all 30 constituent companies. A leading example is the SPDR Dow Jones Industrial Average ETF (DIA). DJIA futures contracts enable traders to speculate on the future value of the index and Options provide the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell the index at a predetermined price in the future. Mutual funds enable investors to buy a share of a diversified portfolio of DJIA stocks thus providing exposure to the overall index.