Dow Jones Industrial Average ends Wednesday slightly lower after Fed leans away from cuts
- Dow Jones jumped a full percent after CPI inflation cooled before receding.
- Fed's "dot plot" shifted away from rate cuts in 2024.
- Fed held rates as expected as the market wrestles with odds of September rate cut.
The Dow Jones Industrial Average (DJIA) soared over 350 points in early Wednesday trading after US Consumer Price Index (CPI) inflation receded faster than expected but returned to the day's opening bids near 38,780.00 before slipping further into the red in the midweek market session. The DJIA ended Wednesday on the back foot, shedding 35 points and closing down around one-tenth of one percent.
Powell speech: Unexpected weakness in the labor market could call for a response
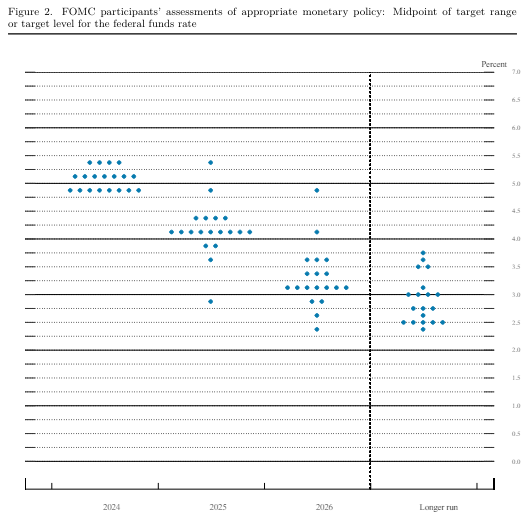
According to the Federal Reserve's (Fed) dot plot of interest rate expectations, fewer members of the Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) see rate cuts in 2024 than before. The FOMC's Summary of Economic Projections (SEP) also expects interest rates to remain higher than previously expected, with 1-year interest rate forecasts now sitting at 4.1% compared to the previous 3.9%.
In 2024, four members of the Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) do not anticipate any rate cuts, while seven members expect only a single quarter-point cut. Eight FOMC voters still foresee two cuts for the year, signifying a shift in the summary of FOMC rate expectations from previous forecasts.
Read more: Jerome Powell speaks on policy outlook after keeping interest rate steady in June.
Federal Reserve Chair Jerome Powell stated in his prepared speech that although there has been an improvement in the balance between employment and overall inflation, the Fed is still cautious and has not yet become confident enough in the progress of inflation to consider cutting rates. Powell also mentioned that inflation has decreased significantly but continues to be too high.
US CPI inflation cooled to 0.0% MoM in May, below the forecast 0.1% and receding even faster from the previous month’s 0.3%. Core CPI ticked down to 3.4% YoY, below the forecast of 3.5% and dropping away from the last period’s 3.6%. With CPI inflation figures easing further, investor sentiment is leaning further into hopes of a September rate cut.
Dow Jones news
The Dow Jones is broadly tilted towards the downside on Wednesday, with over two-thirds of the Dow Jones' constituent securities seeing red post-FOMC. Gains are being led by Apple INC. (AAPL), rising 6% to $219.52 per share as investors pin their hopes on Apple's announced integration of ChatGPT into its iOS software. Salesforce Inc. (CRM) backslide -2.3% to $235.40 per share to lead losses on the Dow Jones for the day.
Dow Jones technical outlook
Wednesday’s CPI-fueled rally briefly peaked above 39,120.00 before risk appetite chilled and sent the Dow Jones back into the day’s opening range near 38,790.00. The major equity index remains mired in near-term congestion at the 200-hour Exponential Moving Average (EMA) at 38,866.60. Bidders have managed to price in a technical rebound from the week’s low bids near 38,400.00, but technical resistance is building from multiple rejections from chart regions north of the 39,000.00 handle.
Dow Jones hourly chart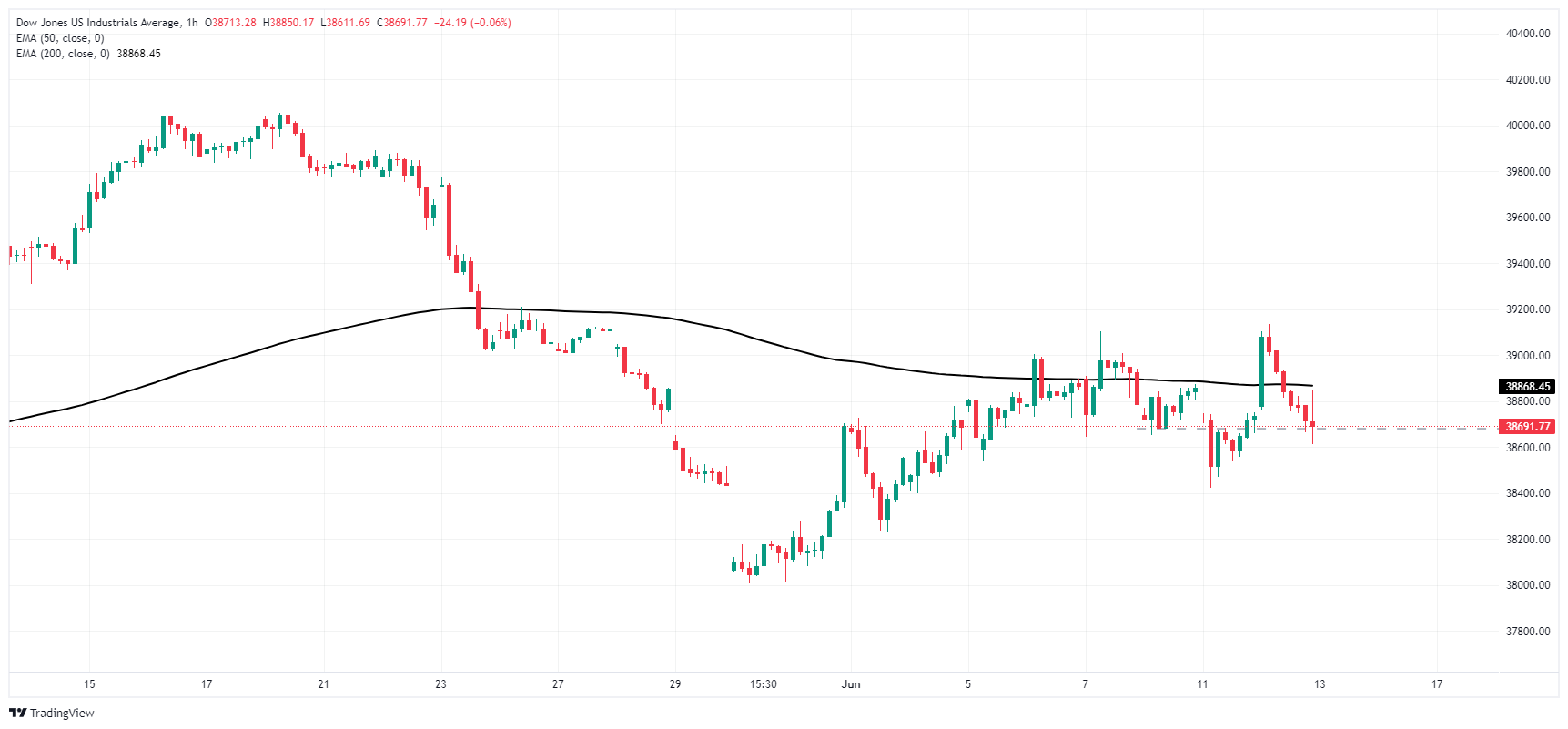
Dow Jones daily chart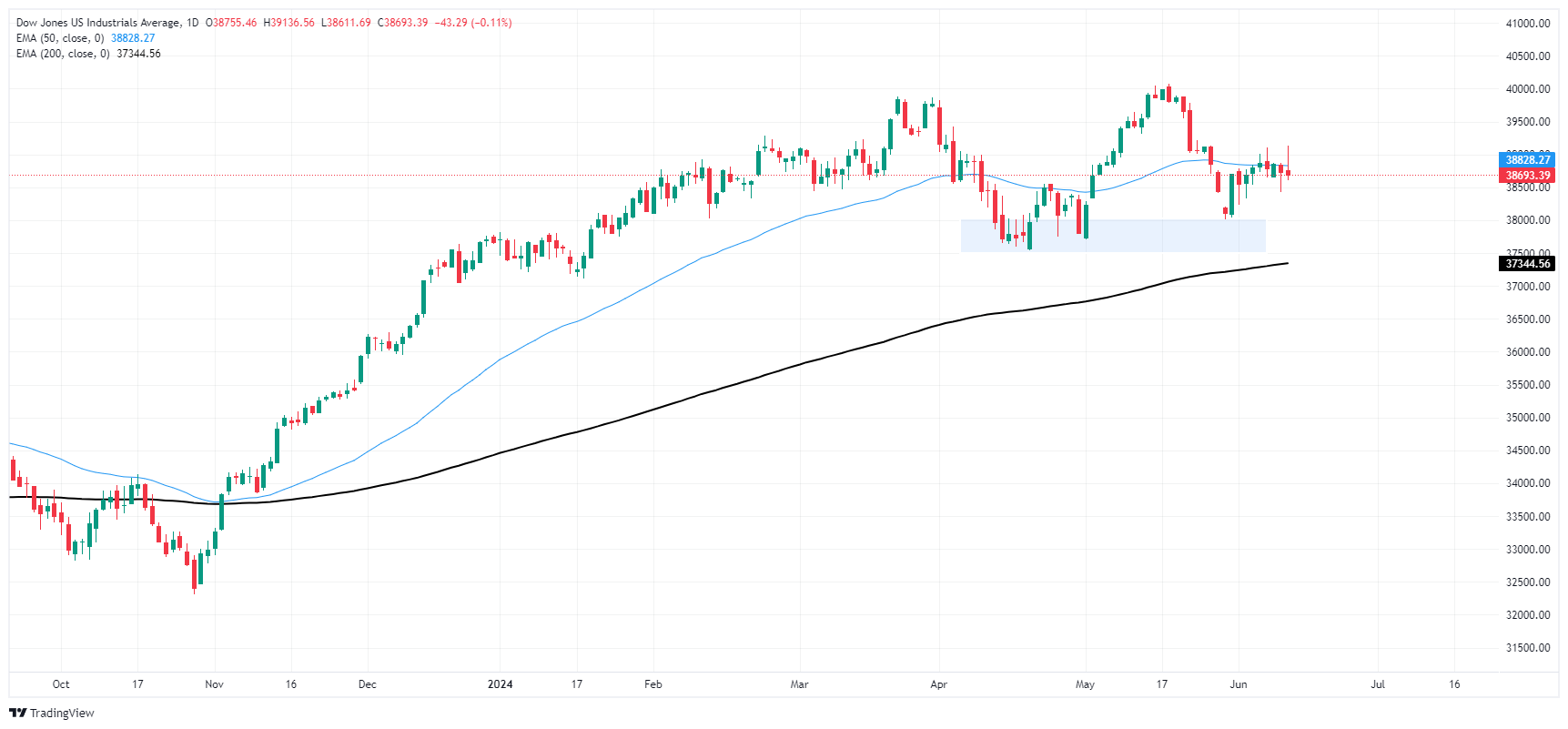
Dow Jones FAQs
The Dow Jones Industrial Average, one of the oldest stock market indices in the world, is compiled of the 30 most traded stocks in the US. The index is price-weighted rather than weighted by capitalization. It is calculated by summing the prices of the constituent stocks and dividing them by a factor, currently 0.152. The index was founded by Charles Dow, who also founded the Wall Street Journal. In later years it has been criticized for not being broadly representative enough because it only tracks 30 conglomerates, unlike broader indices such as the S&P 500.
Many different factors drive the Dow Jones Industrial Average (DJIA). The aggregate performance of the component companies revealed in quarterly company earnings reports is the main one. US and global macroeconomic data also contributes as it impacts on investor sentiment. The level of interest rates, set by the Federal Reserve (Fed), also influences the DJIA as it affects the cost of credit, on which many corporations are heavily reliant. Therefore, inflation can be a major driver as well as other metrics which impact the Fed decisions.
Dow Theory is a method for identifying the primary trend of the stock market developed by Charles Dow. A key step is to compare the direction of the Dow Jones Industrial Average (DJIA) and the Dow Jones Transportation Average (DJTA) and only follow trends where both are moving in the same direction. Volume is a confirmatory criteria. The theory uses elements of peak and trough analysis. Dow’s theory posits three trend phases: accumulation, when smart money starts buying or selling; public participation, when the wider public joins in; and distribution, when the smart money exits.
There are a number of ways to trade the DJIA. One is to use ETFs which allow investors to trade the DJIA as a single security, rather than having to buy shares in all 30 constituent companies. A leading example is the SPDR Dow Jones Industrial Average ETF (DIA). DJIA futures contracts enable traders to speculate on the future value of the index and Options provide the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell the index at a predetermined price in the future. Mutual funds enable investors to buy a share of a diversified portfolio of DJIA stocks thus providing exposure to the overall index.