Mexican Peso climbs as CPI threatens to delay Banxico cuts
- Mexican Peso strengthens for seventh session with USD/MXN down 0.44%, sparked by high inflation.
- Banxico Deputy Governor Borja adopts neutral stance, despite emphasizing that policy is restrictive.
- Banxico’s minutes to address disinflation forces, growth disappointments, and potential downside risks in upcoming meeting.
The Mexican Peso extended its rally for the seventh consecutive session on Wednesday after inflation got close to 5%, which might deter the Bank of Mexico (Banxico) from easing policy at the upcoming monetary policy meeting in August. Therefore, the USD/MXN continued to edge lower and traded at 17.83, a loss of 0.44%.
Mexico’s inflation, as measured by the Consumer Price Index (CPI), was higher than expected in June, hitting 4.98%, above estimates of 4.84%. This triggered a reaction amongst Banxico’s policymakers with Deputy Governor Jonathan Heath writing on X that June’s inflation data was “very worrying.”
Recently, Deputy Governor Galia Borja said, “It's prudent not to make hasty decisions” regarding monetary policy. She’s adopted a more neutral stance, adding that officials must be patient, though she added that the current policy is “undoubtedly restrictive.”
On Thursday, Banxico will reveal its latest monetary policy minutes. Analysts at JP Morgan wrote, “We expect the minutes to elaborate on both disinflation forces and some of the upside risks embedded in the ongoing MXN re-adjustment, and the forces behind growth disappointments.”
They added that Banxico’s board is expected to acknowledge the “underwhelming growth dynamics and downgraded its growth outlook—now openly underscoring downside risks to economic activity.”
Across the border, Federal Reserve (Fed) Chair Jerome Powell appeared at the US House of Representatives and repeated some of Tuesday’s words that the disinflation process is evolving and that the risks of achieving the dual mandate have become more balanced. He added that Fed officials needed good inflation data to lower borrowing costs and that neutral rates must have moved up “at least in the short term.”
Daily digest market movers: Mexican Peso rockets due to high inflation
- According to the National Statistics Agency (INEGI), Mexico’s June inflation figures were higher than expected due to a rise in food prices when most economists expect Banxico to resume lowering interest rates.
- Mexico’s CPI rose from 4.69% YoY to 4.98% in June, while core CPI dipped from 4.21% to 4.13% annually, exceeding the estimated 4.15%.
- Despite the rise in inflation, Capital Economics analysts estimate that the Mexican central bank could cut rates at the August meeting.
- On Monday, the New York Federal Reserve revealed that consumer inflation expectations were lowered from 3.2% to 3% for one year.
- US CPI is foreseen dropping from 3.3% to 3.1% in the 12 months to June, while underlying inflation is projected to stay firm at 3.4% YoY.
- US Dollar Index (DXY), which tracks the value of a basket of six currencies against the US Dollar, advances some 0.16% and is up at 105.17.
- According to the CME FedWatch Tool data, the odds for a September cut are 72%, up from 70% on Tuesday.
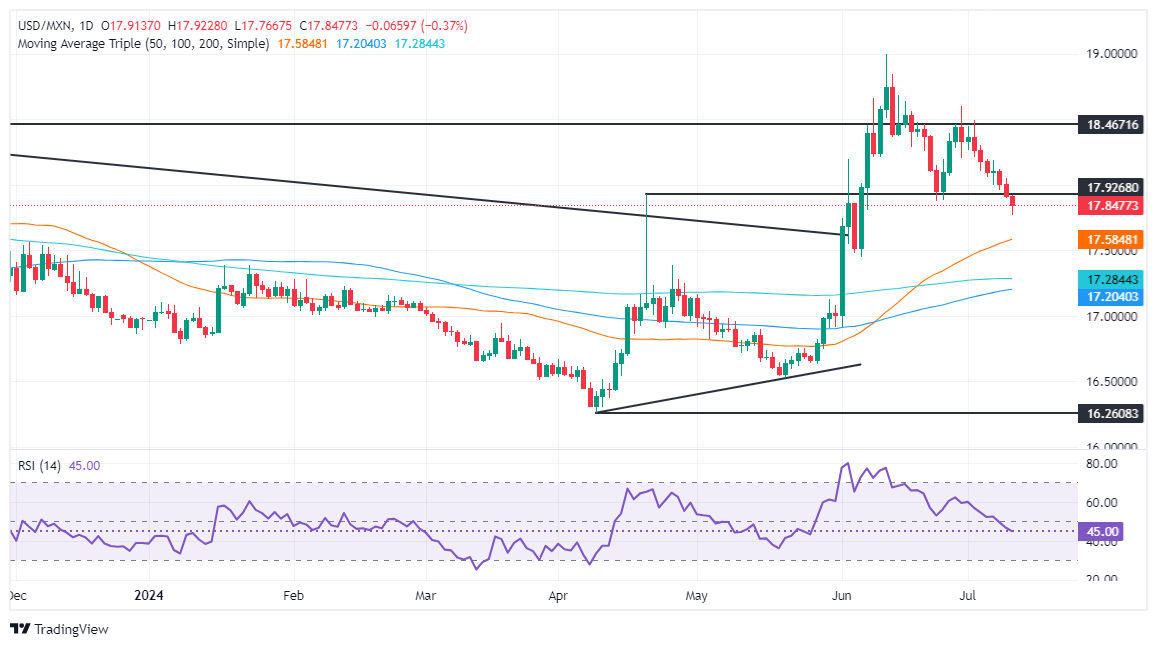
Technical analysis: Mexican Peso appreciates sharply as USD/MXN falls below 17.85
The USD/MXN continued to extend its losses past June 24, the latest cycle low of 17.87, which could pave the way for a deeper correction. Momentum has abruptly shifted in bears’ favor, an indication that sellers will drive the exotic pair price action lower.
If the downtrend continued, the next support would be the confluence of the December 5 high and the 50-day Simple Moving Average (SMA) at around 17.56/57, followed by the 200-day SMA at 17.26. The next floor level would be the 100-day SMA at 17.19.
For a bullish resumption, USD/MXN must surpass 18.10, followed by a rally above the June 28 high of 18.59, allowing buyers to challenge the YTD high of 18.99. Conversely, sellers will need to push the pair below 18.00, which could extend the decline toward the December 5 high-turned-support at 17.56, followed by the 50-day SMA at 17.37.
Mexican Peso FAQs
The Mexican Peso (MXN) is the most traded currency among its Latin American peers. Its value is broadly determined by the performance of the Mexican economy, the country’s central bank’s policy, the amount of foreign investment in the country and even the levels of remittances sent by Mexicans who live abroad, particularly in the United States. Geopolitical trends can also move MXN: for example, the process of nearshoring – or the decision by some firms to relocate manufacturing capacity and supply chains closer to their home countries – is also seen as a catalyst for the Mexican currency as the country is considered a key manufacturing hub in the American continent. Another catalyst for MXN is Oil prices as Mexico is a key exporter of the commodity.
The main objective of Mexico’s central bank, also known as Banxico, is to maintain inflation at low and stable levels (at or close to its target of 3%, the midpoint in a tolerance band of between 2% and 4%). To this end, the bank sets an appropriate level of interest rates. When inflation is too high, Banxico will attempt to tame it by raising interest rates, making it more expensive for households and businesses to borrow money, thus cooling demand and the overall economy. Higher interest rates are generally positive for the Mexican Peso (MXN) as they lead to higher yields, making the country a more attractive place for investors. On the contrary, lower interest rates tend to weaken MXN.
Macroeconomic data releases are key to assess the state of the economy and can have an impact on the Mexican Peso (MXN) valuation. A strong Mexican economy, based on high economic growth, low unemployment and high confidence is good for MXN. Not only does it attract more foreign investment but it may encourage the Bank of Mexico (Banxico) to increase interest rates, particularly if this strength comes together with elevated inflation. However, if economic data is weak, MXN is likely to depreciate.
As an emerging-market currency, the Mexican Peso (MXN) tends to strive during risk-on periods, or when investors perceive that broader market risks are low and thus are eager to engage with investments that carry a higher risk. Conversely, MXN tends to weaken at times of market turbulence or economic uncertainty as investors tend to sell higher-risk assets and flee to the more-stable safe havens.